Rich media is surplus and abundant on the internet. Tons of apps these days deal with rich media. Users spend more time uploading and viewing media content than any other thing.
Cloudinary’s PHP SDK, with which you can easily and speedily upload multiple images and videos in PHP files can help you ramp up quickly while dealing the mechanics of php file uploads and rich media during app development.
This article guides you through the process of uploading PHP files and rich media the easy way.
PHP File Uploads With Cloudinary
The Cloudinary Open-source PHP library utilizes the Cloudinary API which allows for the transmission of any kind of file for safe storage in the cloud. They contain easy-to-use helper methods for these image-related tasks:
- Uploads
- Administration and creation of sprites
- Embeddings
- Generation of URLs for transformations
To get started, do the following:
Step 1. Sign up for a Cloudinary account.
Sign up for Cloudinary’s generous free-tier plan.
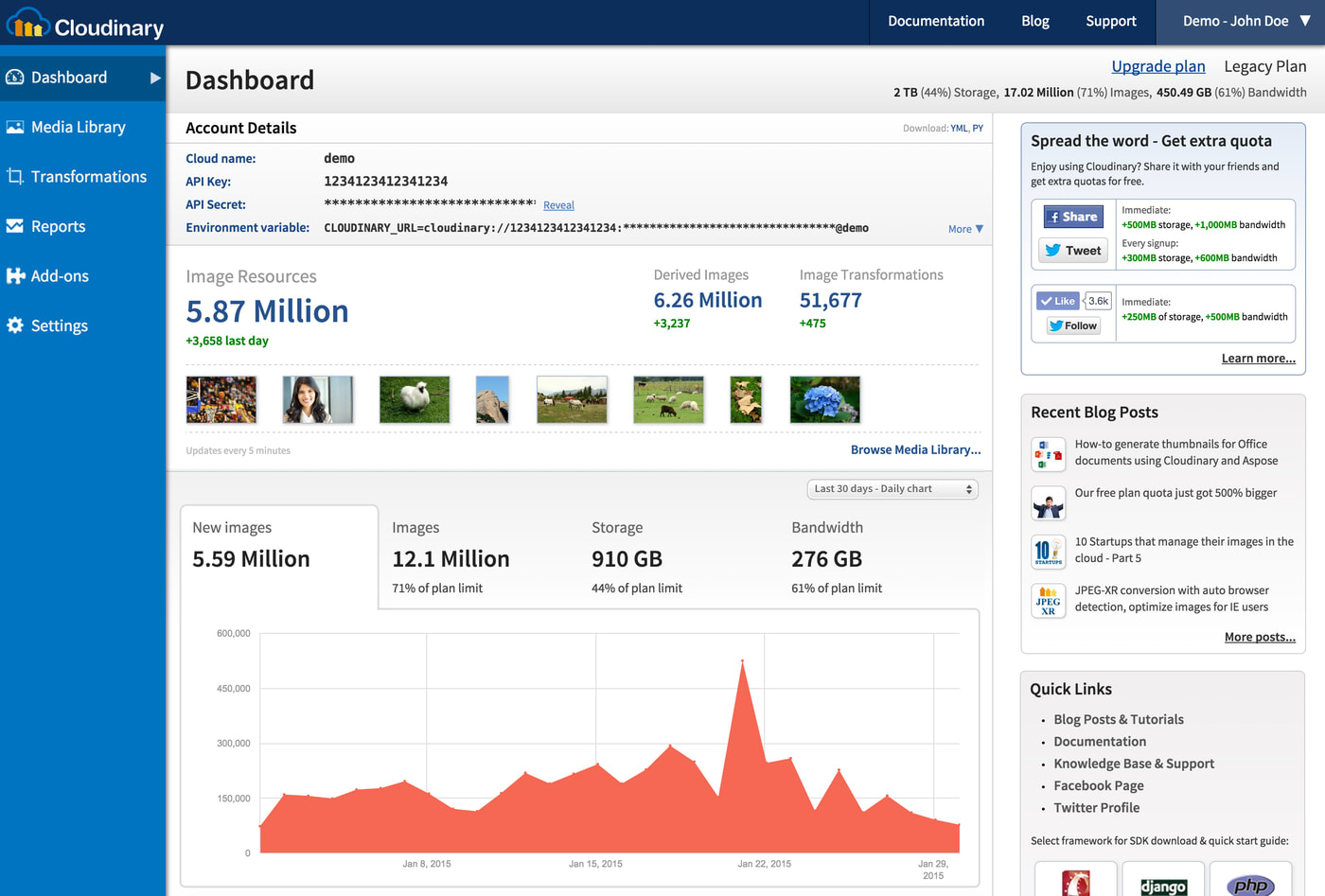 Cloudinary Dashboard: Your cloud name, API key, and API secret are the key values for interacting with Cloudinary’s capabilities.
Cloudinary Dashboard: Your cloud name, API key, and API secret are the key values for interacting with Cloudinary’s capabilities.
Step 2. Install the Cloudinary PHP library.
Fetch the library with Composer. Alternatively, go to Cloudinary’s PHP repository on GitHub, copy all the required files and paste them in your app. Afterwards, then reference them in the script with which to perform the upload, as follows:
/** ** UPLOADING PHP FILES *** // importing the necessary Cloudinary files require 'Cloudinary.php'; require 'Uploader.php'; require 'Helpers.php'; require 'Api.php'; .....
To manage your PHP library’s dependency with Composer, install Cloudinary's PHP library directly from the Packagist repository and update your composer.json file, as follows:
Now install the dependencies, including Cloudinary's PHP package:
For more details, see Cloudinary’s documentation on the PHP SDK.
Step 3. PHP File & Rich Media Uploads to Cloudinary.
You can upload images and other files to Cloudinary in PHP on a server that runs PHP 5.3 or later. Do the following:
First, set up the key values with the config method so that Cloudinary can verify that your account is valid:
\Cloudinary::config(array( "cloud_name" => "my_cloud_name", "api_key" => "my_api_key", "api_secret" => "my_api_secret" ));
.env) file. Alternatively, put them in a file called settings.php and include it in the script that performs the actual uploading.Now upload your images and other files to Cloudinary’s cloud platform:
To upload a local file, e.g.,
my_image.jpg, type:The upload method then returns an associative array whose content is similar to this snippet:
To upload a file from a remote HTTP or HTTPS URL, type:
To upload a file from an S3 bucket, type:
Cloudinary assigns a public ID to each and every uploaded file for transformation and delivery later on.
Here’s the syntax for uploading files with PHP to Cloudinary:
See these examples of what you can pass to the
$optionsargument:A custom public ID:
The name of the uploaded file:
An image, a video, or a RAW file:
For details on all the upload options, see the related Cloudinary documentation.
Conclusion
Uploading PHP images files to Cloudinary] is hassle free. Once you’ve completed that task, you no longer need to store files on your host server. Do take advantage of dedicated cloud-storage services like Cloudinary, which also performs the invaluable task of serving files securely to web apps through content delivery networks (CDNs).
Want to Learn More About File Uploads?
- Automating File Upload and Sharing
- Uploading PHP Files and Rich Media the Easy Way
- AJAX File Upload: Quick Tutorial & Time-Saving Tips
- Impressed by WhatsApp? Clone the WhatsApp Technology to Build a File-Upload App on Android
- Direct Image Uploads From the Browser to the Cloud With jQuery
- File Upload With Angular to Cloudinary
- Uploading Vue Files and Rich Media in Two Easy Steps
- Node.js File Upload to a Local Server Or to the Cloud
- Laravel File Upload to a Local Server Or to the Cloud
- JavaScript File Upload in Two Simple Steps